Continuous and pulsed X-ray generators

The objectives in this field are as follows:
- Establish national references in terms of air kerma (gray) and air and water dose (Sv) of low and medium energy X-ray beams (few keV to 300 keV) used in research, industry or medical applications.
- Improve methods and instruments for measurement of the reference kerma and dose to reduce uncertainty values for these two quantities.
- Calibrate measuring devices, whether active (cavity ionization chambers, semiconductor dosimeters, etc.) or passive (TLD, OSL, etc.) for clients from research, industry or medical fields.
The LNHB’s pool of X-ray generators covers research, industry and medical activities.
Pulsed emission X-ray sources for medical imaging applications
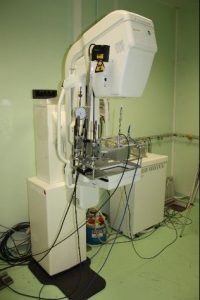 Mammograph: device used for detecting breast cancer
Mammograph: device used for detecting breast cancer
Molybdenum or rhodium anodes
Voltage range: 20 kV to 49 kV
Measuring range in air kerma: 0.5 mGy to 100 mGy
LNHB mammograph
 Radiodiagnosis: apparatus traditionally used for radiography
Radiodiagnosis: apparatus traditionally used for radiography
Tungsten rotating anode
Voltage range: 40 kV to 150 kV
Measuring range in air kerma: 0.01 mGy to 150 mGy
LNHB X-ray tube for radiodiagnostic with its MD03 air chamber
 Phase X: apparatus used in interventional surgery
Phase X: apparatus used in interventional surgery
Tungsten rotating anode, operating in scopy mode
Voltage range: 40 kV to 150 kV
Measuring range in air kerma: 0.01 mGy to 150 mGy
LNHB X-ray tube Phase X type
Continuous emission X-ray sources used in industrial or medical fields (industrial imaging, worker or patient radiation protection, etc.)
X-ray tube Gulmay 160 kV
Tungsten anode
Voltage range: 10 kV to 100 kV
Air kerma measuring range: 5 µGy/s to 5 mGy/s
 X-ray tube Seifert 320 kV
X-ray tube Seifert 320 kV
Tungsten anode
Voltage range: 20 kV to 320 kV
Air kerma measuring range: 5 µGy/s to 5 mGy/s
X-ray tube Seifert 320 kV
In the field of low and medium energy X-ray dosimetry, references are made up of absolute measuring devices for the dosimetry quantity of interest (kerma in air, dose in air or water). These devices correspond to air chambers. Thus, each X-ray tube in the laboratory is equipped with its own reference air chamber:
| Chamber reference | CE98 | MD03 | WK07 | WK06 |
| Facility | Mammograph | Radiodiagnosis Phase X | Gulmay 160 kV | Seifert 320 kV |
| High voltage range (kV) | 20 – 49 | 40 – 150 | 10 – 100 | 20 – 320 |
| Electric field strength (V/cm) | 500 | 345 | 254 | 278 |
| Opening diameter (cm) | 0.505 | 0.997 | 0.5009 | 1.0074 |
| Measuring volume (cm³) | 0.3391 | 3.781 | 0.4028 | 4.7827 |
| Collector electrode width (cm) | 1.693 | 4.844 | 2.0445 | 6.0004 |
| Distance between electrodes (cm) | 5.0 | 14.5 | 11.8 | 18.0 |
| Air thickness for electronic balance (cm) | 6.05 | 20.4 | 7.2 | 31.8 |
Examples of calibrated equipment
– Active measuring systems: cavity ionization chambers, semiconductor detectors (operational dosimeters)
 |
 |
 |
| Cavity ionization chambers | Operational dosimeters | |
– Passive measuring systems: TLD dosimeters, OSL dosimeters, radio films
 |
 |
 |
| Passive dosimeter | TLD sinter | Alanine pellet |
Our job: metrology
dosimetry
Implemented methods for the establishment of national references must be adapted to the radiation type and its intensity. They are based on measurement technics such as calorimetry, ionometry and chemical dosimetry.
Radioactivity
The variety of the emitted radiation and physical forms of the sources oblige to adapt the measurement process in order to establish national references: methods with defined geometries, or 4 π countings geometries, coincidence countings, etc.
